What's new in 2.0
To leverage the new capabilities of Address Manager 2.0 or greater, you must upgrade an existing Early Adopter version of the application created with Configurator 2.0 by using Configurator 2.1.
New updated data model version 2.1
Address Manager 2.0 updates the data model, which is referred to as Data Model 2.1. This data model includes the NENA Required, Recommended and Strongly Recommended layers. Compared to previous data models, fields have been removed and added to the model to align with NENA GIS Data Model v2a. Changes from the previous data model include:
- Alias Name and Feature Name are the same for all feature class and tables.
- Boundary names such as Service Boundary EMS have changed to EMSPolygon to align with NENA.
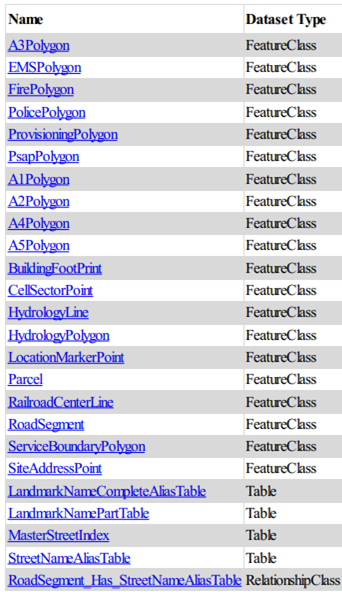
Additional fields support
You may add fields to the data model as needed to support your organization’s requirements. However, do not delete existing fields or remove existing domains. You may add values to existing domains, but do not remove existing domain values. Domain values are populated with NENA recommended values as of the 2.0 release. Some domain values require localization to reflect your aggregator’s local requirements.
| Layer Name Changed From: | Data Model 2.1 Names |
|---|---|
| Road Segment | RoadSegment |
| Incorporated Municipality Boundary | A3Polygon |
| Provisioning Polygon | ProvisioningPolygon |
| PSAP Boundary | PsapPolygon |
| Service Boundary Police | PolicePolygon |
| Service Boundary Fire | FirePolygon |
| Service Boundary EMS | EMSPolygon |
| Master Street Index | MasterStreetIndex |
Removed fields
The following fields were removed from the RoadSegment layer and from the MasterStreetIndex layer. These were legacy fields for storing Street Name Alias values. As per NENA GIS data model, the StreetNameAliasTable is used for storing Street Name aliases. A Street Name Alias tool is planned for a future Address Manager release.
Removed fields:
- rtename1en
- rtename2en
- rtename3en
- rtename4en
- rtename5en
- rtename1fr
- rtename2fr
- rtename3fr
- rtename4fr
- rtename5fr
- rtnumber1
- rtnumber2
- rtnumber3
- rtnumber4
- rtnumber5
- rttype1
- rttype2
- rttype3
- rttype4
- rttype5
Unique index best practices
In Address Manager 2.0, the best practice is to add a unique index after loading the Data Model into your data store. This comprises the following features and tables: |Features | Unique Index| |---|---| |SiteAddressPoint|full_add| |MasterStreetIndex|fullname + municipality| |PolicePolygon|DsplayName| |FirePolygon|DsplayName| |EMSPolygon|DsplayName| |PsapPolygon|DsplayName| |A3Polygon|Inc_Muni|
System requirements
Address Manager 2.0 can be deployed on the following ArcGIS environments:
- ArcGIS Online – Feature Services
- ArcGIS Enterprise 11.1 – Portal Feature Services
- ArcGIS Enterprise 11.1 – Oracle EGDB 19c
- ArcGIS Enterprise 11.1 – PostGres EGDB 3.3
- ArcGIS Enterprise 11.1 – MS SQL Server 2022
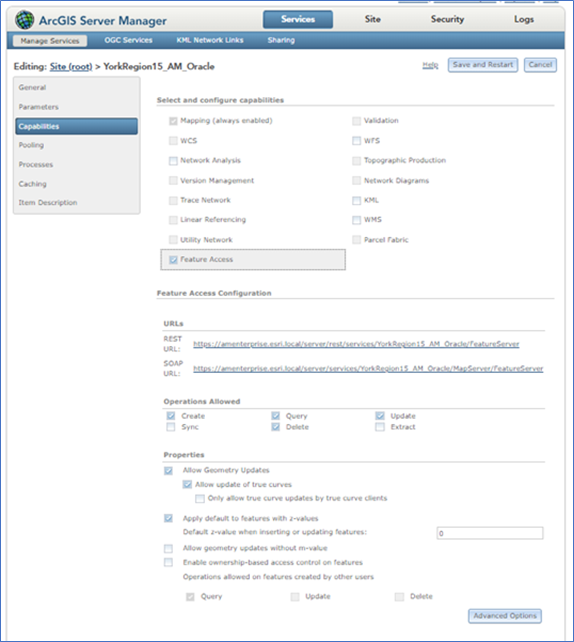
Address Manager is developed with the JSPAPI 4.x. When deploying on an EGDB, the API requires certain settings in ArcGIS Server Manager.
- Check Allow Geometry Updates.
- Check Allow Update of true curves.
- Check Apply default to features with z-values and set the default to 0.
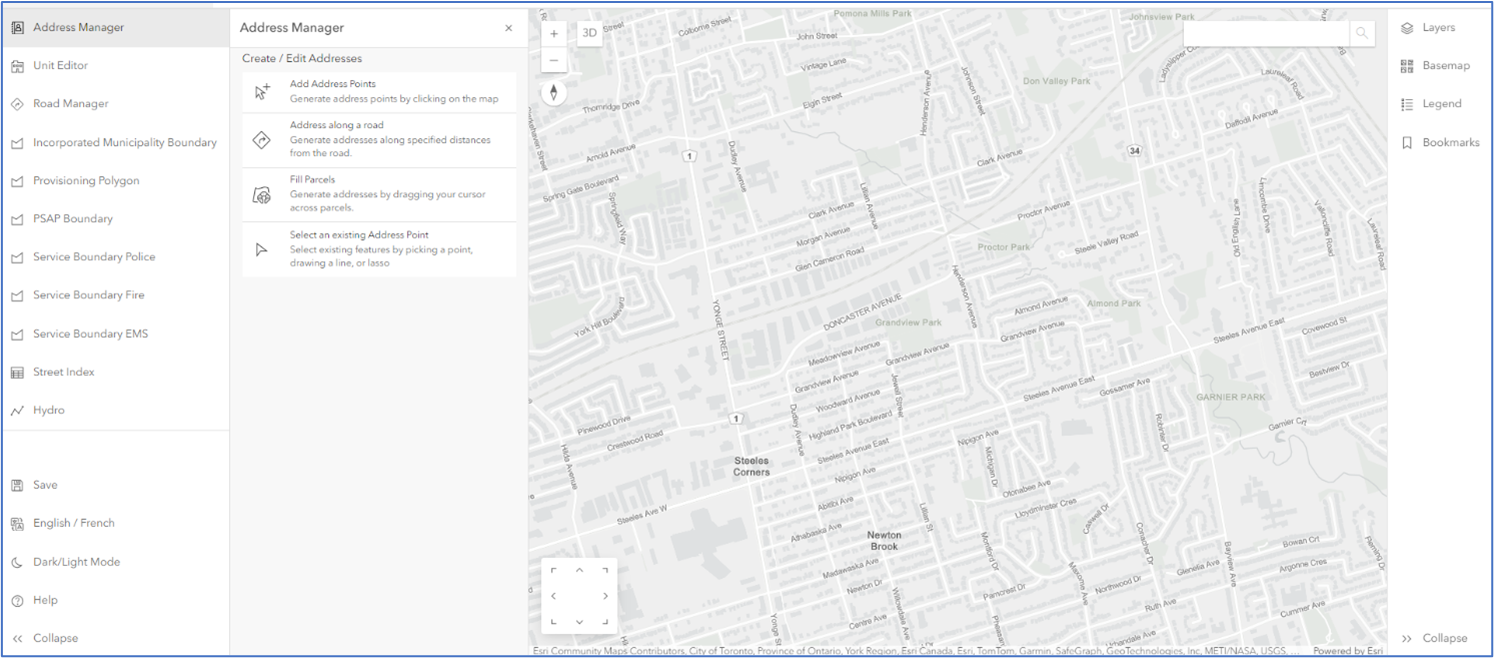
Address Manager capabilities
Address Manager v2.0 introduces a modern interface developed in the Esri Calcite Design System. You should note that Address Manager 2.0 only supports the Data Model 2.1. If you are an existing Address Manager 1.5 user, you must perform an ETL process of your data to the Address Manager Data Model 2.1. After successfully performing this transfer, you can configure a new application with Configurator to generate a new Address Manager 2.0 application.
Configurator 2.0 new enhancements and options
Configurator includes a new default configuration for Address Manager 2.0, which can be used as a starting point for your organization's application. It can be further modified to meet your specific requirements. It will detect your data type and it will update common elements such as feature and field names to match your data source. For example, If your application exists in an Oracle environment, Configurator will update its mixed case field names to match Orcale's uppercase field names requirements.
- The default configuration includes editing tools for all NENA Required NG9-1-1 layers. The MasterStreetIndex is now configurable and included in the default configuration; however, the MasterStreetIndex configuration should not be modified. You can disable this tool and save a new version of the application for users that do not require access to this tool.
- A Tools option appears on the left-side menu panel that includes tools for configuring features or for editing tables of any layer. This also includes the web map layer. These tools can be used to configure separate, customized instances of Address Manager for use by different users. For example, you can configure one instance of Address Manager to allow editing boundary polygons, while another instance of Address Manager is configured to not.
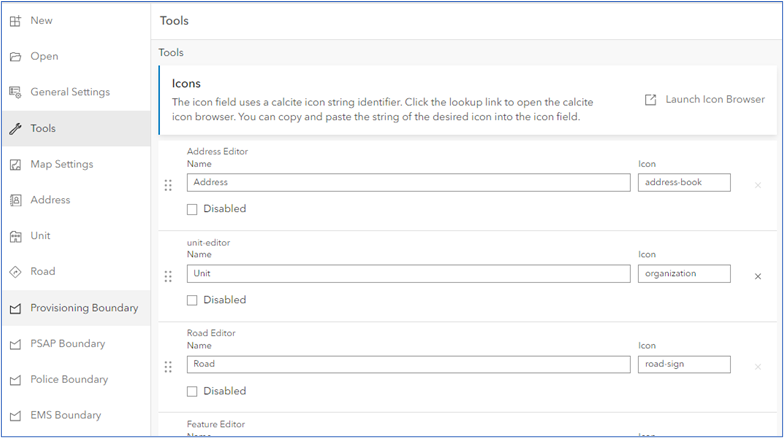
- Several layers and fields in Address Manager 2.0 must exist, which also match NENA fields. These fields should not be removed. Features, such as the MasterStreetIndex table, should not be modified or removed for Address Manager 2.0 to function properly. However, you may add fields required by your organization, or you may add layers to the web map from other sources.
Mandatory RoadSegment fields:
| Address Manager | Description |
|---|---|
| l_hnumf | Left House Number From |
| l_hnuml | Left House Number Last |
| l_adddirfg | Left Address Range Direction |
| parity_l | Left Address Parity |
| r_hnumf | Right House Number From |
| r_hnuml | Right House Number Last |
| r_adddirfg | Right Address Range Direction |
| parity_r | Right Address Parity |
| ReasonForChange | Reason For Change |
| fullname | Full Road Name |
Mandatory SiteAddressPoint fields:
| Address Manager | Description |
|---|---|
| full_add | Full Address |
| pointtype | NENA refers to this field as the “Placement Method”. Address Manager requires “pointtype” as a mandatory field to enable address placement tools. The domain table must match the Address Manager domain table. |
Common mandatory fields:
| Address Manager | Description |
|---|---|
| currentstatus | Current Status |
| createddate | Created Date |
| revisiondate | Revision Date |
| approveddate | Approved Date |
| retireddate | Retired Date |
| activedate | Active Date |
- You can refer to the spreadsheet document: AM21DataModelNENA. For each feature and table, you will find two columns named NENA Field and Address Manager Mandatory Field.
- Yes under the NENA Field indicates the field is part of the NENA GIS Data Model and must not be removed or altered.
- Yes under the Address Manager Mandatory Field indicates the field is mandatory for Address Manager v2.0 and must not be removed or altered.
- Attribute Picklist is a feature level configuration that applies to fields for any feature type: lines, points, polygons, attribute tables. When enabled, Address Manager 2.0 displays a pull-down list of values from a table or feature defined by the Attribute Picklist. In the Attribute Picklist Configuration panel, you can define an attribute or feature table and a pick list field to select a value.
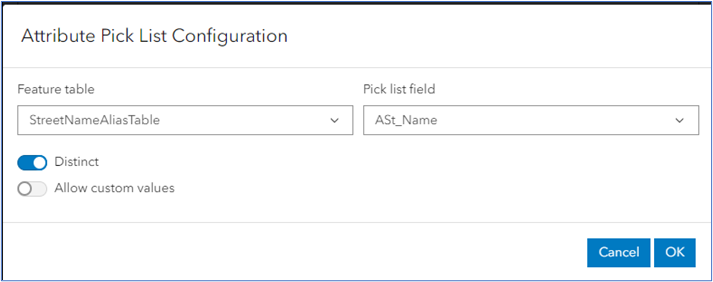
Attribute Transfer is a feature level configuration that only applies to point features (e.g., Site Address Point). This configuration instructs Address Manager 2.0 to transfer a value from a polygon to a specified field. Address Manager's default configuration already defines an Attribute Transfer for SiteAddressPoint to transfer the PID value from the parcel polygon feature to the parcelid field in SiteAddressPoint. Some examples include the following:
- When an address point falls inside a postal code polygon, the Attribute Transfer configuration transfers the postal code value from the postal code polygon to the SiteAddressPoint's postal code field.
- When an address point falls inside a parcel polygon, it transfers the parcel ID value from the parcel polygon to the SiteAddressPoint Parcel ID field.
- When an address point falls inside a community polygon, it transfers the community name from the community polygon to the SiteAddressPoint community field.
Calculate includes the Attribute Transfer directive, as it specifies a transferable value from a specified polygon when a point feature falls inside it.
- Maximum, Starting at calculate directive generates a unique number, which is only applicable to fields with an integer data type.
- Apply after Commit directive generates a data value after the feature is added to the feature service. Typically, this directive only applies to NGUID fields, which includes the ArcGIS GlobalID value; however the GlobalID is generated after the feature is inserted to the feature service. Apply after Commit directs the Address Manager 2.0 to update the NGUID field after the feature is inserted and a GlobalID is generated.
- Apply Immediately generates a data value when the feature is inserted into the feature service.
- Master Road Name Lookup picks a value from the MasterStreetIndex table. When you activate this option, Address Manager will prompt you to define which fields from the MasterStreetIndex table should be transferred. Field transfer options can be set to Automatic or Manual.
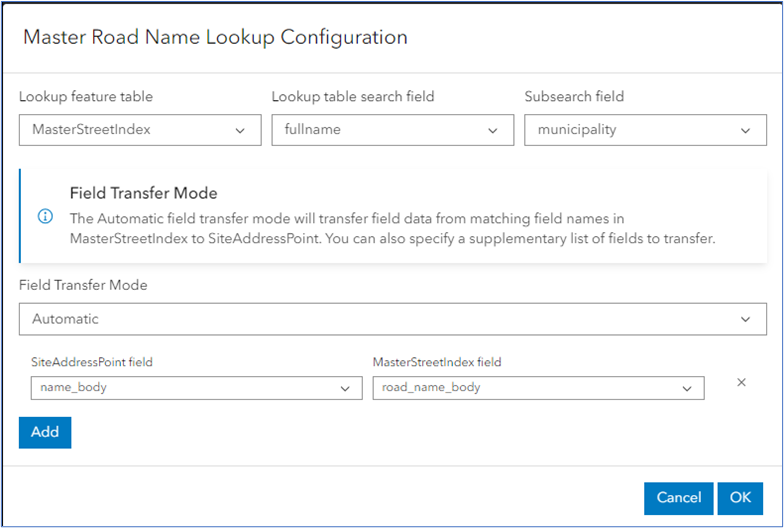
Master Road Name Lookup Configuration panel
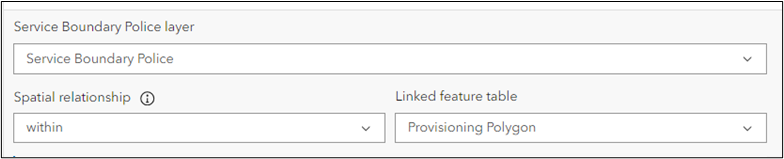
- Spatial relationship allows you to apply a spatial relationship between two NG9-1-1 boundaries. For example, if the feature layer for this tool is a PolicePolygon, you set the spatial relationship to within and set the linked feature table to ProvisioningPolygon. When you create a new PolicePolygon it must not overlap the ProvisioningPolygon. Spatial relationships checks are not performed in 2.0, as these will be implemented in a future release. However, you should not change these relationships.
- Units Editor interface adds address units to a multistory building that are related to a primary address. These address units are stored in the SiteAddressPoint layer. When a unit is added It inherits attributes from the primary address. Calculated fields are applied separately for each unit in the following order:
- All matching fields from primary address are transferred to the units SiteAddressPoint feature.
- Then default values are applied to the units.
- Then any Arcade script defined on the SiteAddressPoint are executed (i.e., any scripts for NGUID such as AutoGen number).
- Unit Editor is preconfigured in Address Manager 2.0, and should not be modified. You can, however, add fields to the display order, but you should not change or delete the existing configuration of the unit's field attributes.
NENA NG9-1-1 GIS data layers
Address Manager 2.0 includes these GIS data layers defined by the NENA NG9-1-1 GIS Data Model. They are shown in the lists below:
- Required layers must be available for NGCS to process a 9-1-1 call on an ESInet, the ECRF and LVF, and for functionality of the SI.
- RoadCenterLine (RoadSegment)
- SiteStructureAddressPoint (SiteAddressPoint)
- PsapPolygon
- FirePolygon
- PolicePolygon
- EmsPolygon
- ProvisioningPolygon
- Strongly Recommended layers may aid in NGCS functionality, may be used for call taking and dispatch operations, and are used in other operations.
- StreetNameAliasTable
- LandmarkNamePartTable
- LandmarkNameCompleteAliasTable
- A1Polygon
- A2Polygon
- A3Polygon
- A4Polygon
- A5Polygon
- Recommended layers will not be provisioned into the LVF or the ECRF but can enhance the GIS data for NG9-1-1 and E9-1-1 call taking and dispatch operations.
- RailroadCenterLine
- HydrologyLine
- HydrologyPolygon
- CellSectorPoint
- LocationMarkerPoint
Provisioning polygon
Address Manager 2.0 also includes the ProvisioningPolygon layer, which defines the area of GIS data provisioning responsibility. When delineating a Provisioning Polygon, priority should be given to the geographic extent authorized for a GIS Data Provider to submit required GIS data. When a GIS Data Provider submits data to a local aggregator (i.e., a Telco or Regional Aggregator), this data must only include GIS data for their geographic area of responsibility, and it must only be within the extent of the provisioning boundary.
NGUID format
The NGUID format contains a layer indicator, which identifies the feature type it represents. It is comprised of the following and formats and components:
urn:emergency:uid:gis:Layer Indicator:Local Unique ID:Agency ID
urn:emergency:uid:gisis a standardized unique prefix that defines the class of IDs associated with GIS data.- The Layer Indicator is the GIS data layer the feature is associated with.
- The Local Unique ID is generated for the GIS Data Provider and is a locally assigned ID. It can be a numeric, text, or a combination. the Local Unique ID must be unique within the GIS Data Provider’s dataset. Address Manager 2.0 sets the Local Unique ID as the GlobalID.
- The Agency ID is the Agency Identifier which is a domain that represents the GIS Data Provider (e.g., toronto.ca).
Core Address Manager features
| GIS Layer Name | Layer Indicator (lower case) |
|---|---|
| SiteAddressPoint | ssap |
| RoadSegment | rcl |
| PolicePolygon | pol |
| FirePolygon | fire |
| EMSPolygon | ems |
| A1Polygon | a1 |
| A2Polygon | a2 |
| A3Polygon | a3 |
| A4Polygon | a4 |
| A5Polygon | a5 |
| ProvisioningPolygon | provisioning |
| PsapPolygon | psap |
Other service polygons stored in ServicePolygon
| GIS Layer Name | Layer Indicator (lower case) |
|---|---|
| FireForestPolygon | firefor |
| FireAirportPolygon | fireair |
| FireMilitaryPolygon | firemil |
| FirePrivatePolygon | fireprivt |
| EmsPrivatePolygon | emsprivt |
| EmsAirPolygon | emsair |
| EmsMilitaryPolygon | emsmil |
| PoisonControlPolygon | poisoncntl |
| MountainRescuePolygon | mntnresc |
| CoastGuardPolygon | coastg |
| PoliceCountyPolygon | polcnty |
| PoliceStateProvincialPolygon | polstprovl |
| PoliceFederalPolygon | polfed |
| PoliceFederalFbiPolygon | polfedfbi |
| PoliceFederalRcmpPolygon | polfedrcmp |
| PoliceFederalSecretServicePolygon | polfedscrtsrv |
| PoliceFederalDeaPolygon | polfeddea |
| PoliceFederalMarshalPolygon | polfedmars |
| PoliceFederalCustomsBorderProtectionPolygon | polfedcustbprtcn |
| PoliceFederalImmigrationCustomsPolygon | polfedimmcust |
| PoliceFederalAtfPolygon | polfedatf |
| PoliceFederalParkPolygon | polfedpark |
| PoliceFederalDiplomaticSecurityPolygon | polfeddipscrty |
| PoliceFederalProtectiveServicePolygon | polfedprttvsrv |
| PoliceSheriffPolygon | polsheriff |
| PoliceMilitaryPolygon | polmil |
| PoliceCampusPolygon | polcamp |
| PolicePrivatePolygon | polprivt |
| PoliceAirportPolygon | polair |
| PoliceHousingPolygon | polhous |
| PoliceParkPolygon | polpark |
| StreetNameAliasTable | strna |
| LandmarkNamePartTable | lnmknamepart |
| LandmarkNameCompleteAliasTable | lnmknamecompa |
| RailroadCenterLine | rrcl |
| HydrologyLine | hydl |
| HydrologyPolygon | hydpgn |
| CellSectorPoint | cellsect |
| LocationMarkerPoint | locmark |
GlobalID differences between ArcGIS Online and ArcGIS Enterprise
Address Manager 2.0 adheres to the GlobalID format of the source datastore.
- ArcGIS Online stores a GlobalID in lowercase without curly brackets. The NGUID will reflect this format when using Address Manager with ArcGIS Online.
urn:emergency:uid:gis:ssap:6cbf4573-4ca8-472b-915f-7ee954c445d0:anytown.ca
- ArcGIS Enterprise stores a GlobalID in uppercase and includes curly brackets. The NGUID will reflect this format when using Address Manager 2.0 with ArcGIS Enterprise.
urn:emergency:uid:gis:ssap:{440B0996-D68E-4F52-B887-223F470A7571}:anytown.ca